PR Newswire, CERRITOS, CA, March 30, 2016
This world’s first FDA clearance for tissue regeneration is groundbreaking in that Millennium Dental has demonstrated that tissues lost to disease can be fully regenerated, including return to functional health. www.TrueRegeneration.com
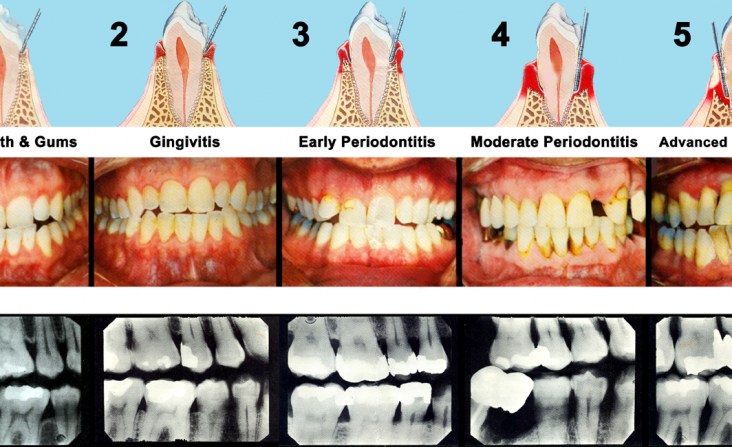
The pathway of tissue regeneration researched and cleared was tissues lost and destroyed as a result of infectious, inflammatory periodontal disease. This suggests there may be other pathways to tissue regeneration in the body that could now be investigated.
Key Facts
- First FDA clearance of functional tissue regeneration as a result of a protocol and device
- True Regeneration™ of periodontal tissue lost to gum disease – new alveolar bone, new cementum, new periodontal ligament
- 85% of U.S. adults have some level of gum disease (periodontal disease)
- 50% of U.S. adults have moderate to severe gum disease. Of this group, 40% don’t know they have the disease, and only 3% accept traditional treatment.
- True Regeneration™ only achievable with the LANAP® protocol
- LANAP protocol = LAR (laser assisted regeneration)
(FDA 510(k)-151763).
True Regeneration returns function to diseased areas naturally
Repair, for example, is not regeneration. Regeneration is return to normal architecture and functional health; repair is not. True Regeneration™ can be obtained despite the presence of periodontal disease – one of the most stubborn, persistent, and widespread infectious diseases according to the Surgeon General and the CDC 2010 NHANES report in the Journal of Dental Research on the prevalence of periodontal disease. (J Dent Res 89(11):1208-1213, 2010).
The LANAP/LAR procedures with the PerioLase MVP-7 achieve these results with:
- No biologics
- No growth factors
- No exogenous bone grafts
- No foreign membranes
- No scaffolding
- No stitches
MDT has trained 2,000 credentialed LANAP regenerative specialists that include general practitioners and periodontists alike. LANAP regenerative specialists are found in every U.S. state and major metropolis, as well as Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Guam.
Quotes
Dawn M. Gregg, DDS, Director of Training for the Institute for Advanced Laser Dentistry, states, “This new FDA indication for use changes the meaning of ‘return to periodontal health.’ No longer is return to periodontal health defined by filling holes or cutting away tissue. The FDA clearance reflects what we understood from two human histological studies – the LANAP protocol produces both periodontal tissue regeneration and function to previously diseased tissues.”
Andrew Sullivan, DDS, Chair of Periodontics at Rutgers, says, “As Chair of the Periodontics Department of Rutgers School of Dental Medicine, I was delighted to learn Millennium has received acknowledgement from the FDA that LANAP can achieve the “Gold Standard” in periodontal therapy – true periodontal regeneration. Rutgers periodontal residents are trained in the most advanced techniques, including the LANAP protocol.”
ABOUT MILLENNIUM DENTAL TECHNOLOGIES INC.: Headquartered in Cerritos, Calif., Millennium Dental Technologies, Inc., is the developer of the LANAP® protocol for the regeneration of periodontal tissues destroyed by gum disease, and the manufacturer of the PerioLase® MVP-7™, the world’s first pulsed Nd:YAG digital dental laser. By providing a patient and doctor friendly experience with virtually no pain, bleeding, or post-procedure infection, MDT’s FDA-cleared and patented LANAP® / LAR™ protocol removes the fear from gum disease treatment, offering a vastly less painful and less invasive, full-mouth regenerative treatment alternative to conventional scalpel/suture flap surgery. The PerioLase® MVP-7™ is a 6-watt, free-running, variable-pulsed Nd:YAG dental laser featuring digital technology and 7 pulse durations in the 1064 nanometer wavelength, giving it the power and versatility to perform a wide range of soft- and hard-tissue laser procedures. The PerioLase® MVP-7™ is also developed for the LAPIP™ protocol, for the treatment of ailing and failing implants. Established in 1994, the company’s founding clinician, Robert H. Gregg II DDS, and wife Dawn M. Gregg DDS, continue to operate the company with the founding vision: “The Patient Comes First.” For more information, visit www.lanap.com.
CONTACT:
Rachel Moody
Millennium Dental Technologies, Inc.
(562) 860-2908
rmoody@lanap.com